Cozy Bear (APT29) Constant presences
Alias: IRON RITUAL, IRON HEMLOCK, NobleBaron, Dark Halo, StellarParticle, NOBELIUM, UNC2452, YTTRIUM, The Dukes, Cozy Bear, CozyDuke, SolarStorm, Blue Kitsune, UNC3524, Midnight Blizzard, APT29
In early 2024, the the German political alliance of the CDU and CSU parties was targeted by the Russian state-sponsored hacking group APT29, also known as Cozy Bear. This sophisticated attack was followed by another in late June 2024, when APT29 compromised TeamViewer, a widely-used remote access software provider. These incidents underscore the persistent threat posed by Russian cyber espionage groups. Alongside Cozy Bear, other groups like APT28 (Fancy Bear), Voodoo Bear, Primitive Bear, and Venomous Bear employ advanced tactics to infiltrate and extract data from their targets. Understanding these methods is crucial for strengthening global cybersecurity defenses against such formidable adversaries.
Cozy Bear (APT29)
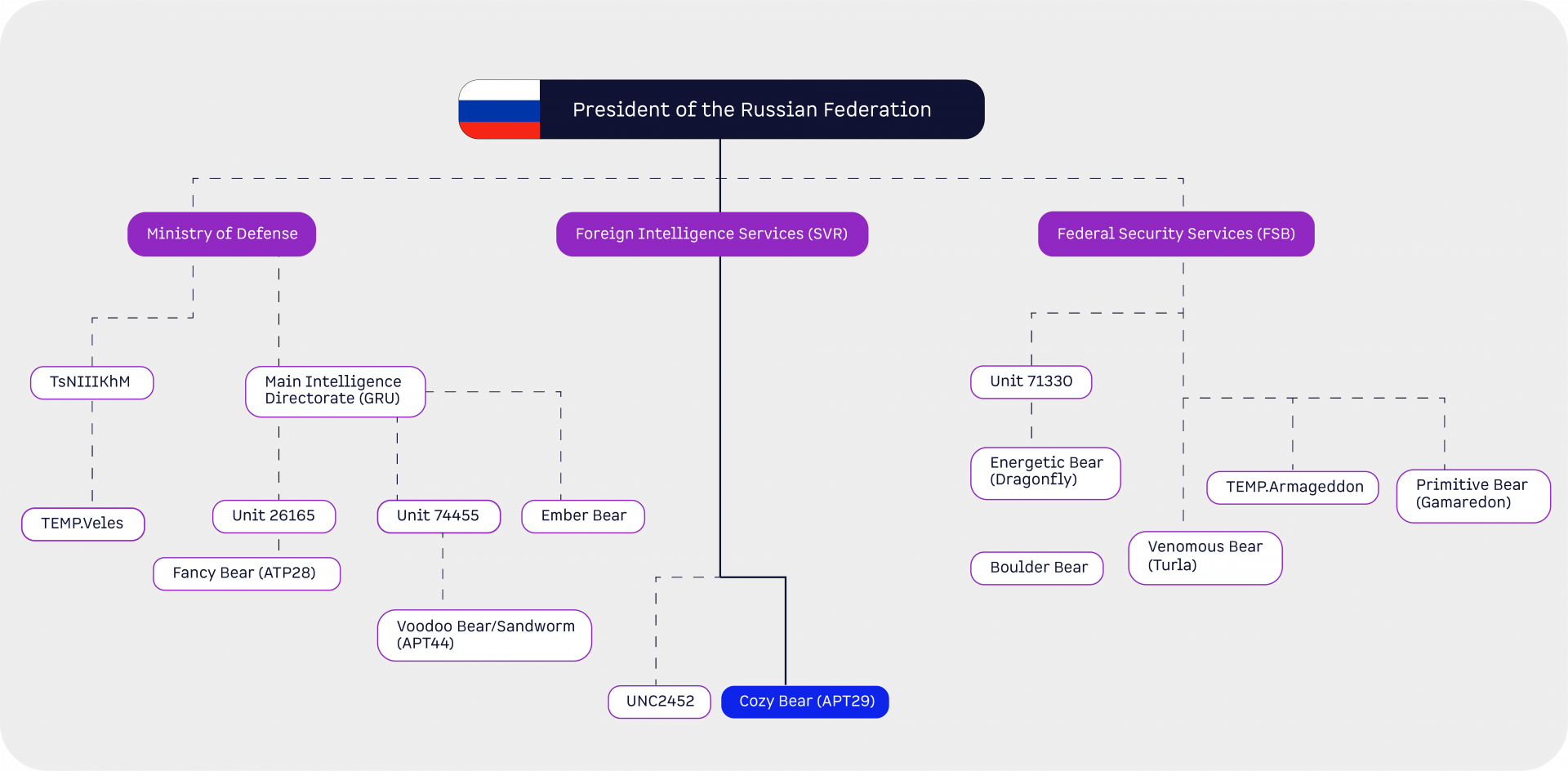
APT29 (Advanced Persistent Threat) or Cozy Bear is a Russian hacker group that belongs to “Putin's Bears” and is subordinate to the Russian foreign intelligence service (SVR).
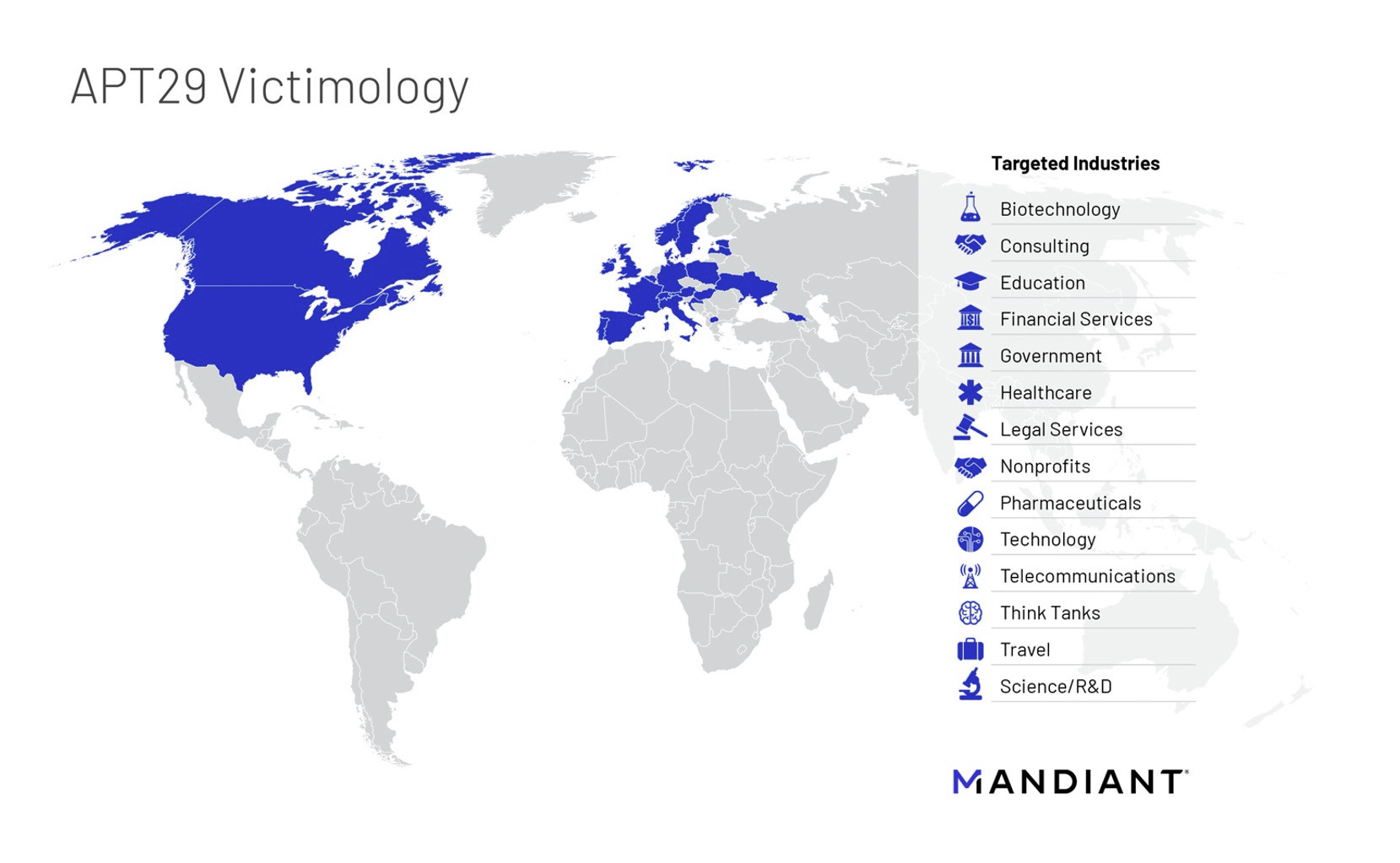
The goal of the state-sponsored group is primarily espionage and data theft. APT29's attacks often target government networks themselves, presumably because of the state sponsor, as well as the healthcare sector, travel and many others.
https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/threat-intelligence/unc2452-merged-into-apt29?hl=en
Different software and techniques have been used over the years.
One example of such malware is EnvyScout, which is used for spearphishing attachments (Tactics Initial Access) or for executing various actions in the Azure and M365 environment via Microsoft Graph API (Tactics Execution). This malware is also used by the hacker group TeamTNT, among others. Other tools include FoggyWeb (Backdoor), GoldFinder (command-and-control (C2)), NativeZone (distributed wide-scale malicious email campaign) and WellMess (Remote Access Trojan)
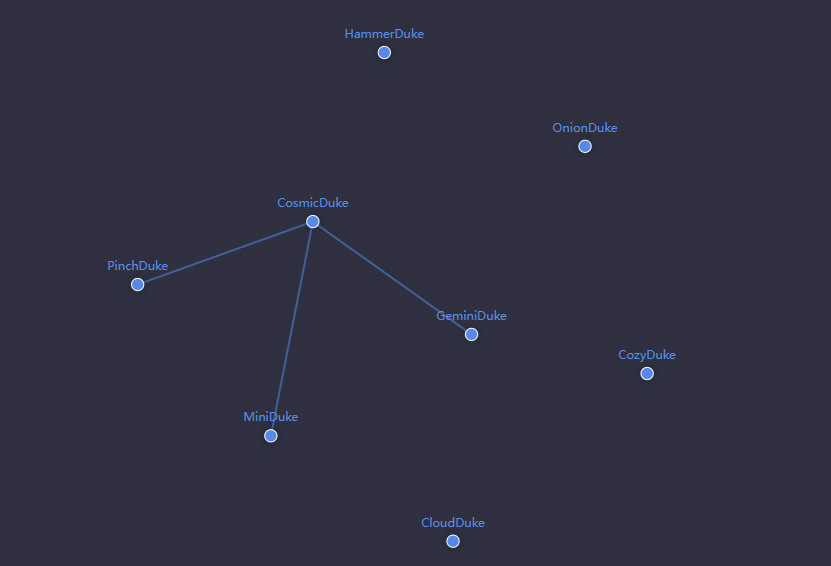
Different malware was also used in the "Operation Ghost" (from 2013 to 2019) and "SolarWinds Compromise" (from 2019 to 2021) campaigns. These include, as you can see in the APT Ecosystem graphic, RegDuke, PolyglotDuke, MiniDuke and FatDuke in "Operation Ghost". Malware such as SUNBURST, SUNSPOT and TEARDROP were used in the SolarWinds Compromise campaign.
Attacks
This year in particular, it is noticeable that more and more larger companies are becoming the target of attacks that can be linked to APT29. These include attacks on the CDU, but also on TeamViewer
CDU
First and foremost, the the German political alliance of the CDU and CSU parties was targeted by the Russian hacker group in February 2024.
The CDU is a Christian democratic, conservative and economically liberal party that was founded between 1945 and 1950.During February,
the following email was sent to various members of this the German political alliance:

https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/threat-intelligence/apt29-wineloader-german-political-parties?hl=en
This is an email inviting people to a dinner on March 1 at 7 pm. In addition, this invitation contains a request to click on a link to register for this event or to fill out a questionnaire. There is also a second link to the information required for this event and a form. According to Mandiant, this is the first German-language phishing email from this group, which indicates that the group's procedures are constantly changing.
If one of the links is clicked on, a malicious ZIP file is opened. This file contains a ROOTSAW dropper that links to the compromised website “hxxps://waterforvoiceless[.]org/invite[.]php”. This website is controlled by APT29.
In the next step, ROOTSAW, which is also called EnvyScout and has been used in previous APT29 operations, delivers another CDU webpage that makes the email look real.

https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/threat-intelligence/apt29-wineloader-german-political-parties?hl=en
The final step is a request to download a file that retrieves the WINELOADER payload from “waterforvoiceless[.]org/util[.]php”.
The only question is what exactly WINELOADER is and where this malware comes from. This often makes analysis much easier.
WINELOADER, which Mandiant says is probably a variant of the BURNTBATTER and MUSKYBEAT code families and can be traced back to APT29, is a backdoor that first appeared at the end of January 2024. It is believed that this WINELOADER attacked diplomatic facilities in Germany, India, Italy, Latvia, Peru and the Czech Republic at the end of January 2024. This is where the Indian ambassador was invited to a wine tasting, which probably explains the name of this backdoor. The screenshot shows that the structure of the email to the CDU and this one look very similar, which reinforces the suspicion that it is the same hacker group.

https://www.zscaler.com/blogs/security-research/european-diplomats-targeted-spikedwine-wineloader
Zscaler has analyzed the WINELOADER file, which was also used in the CDU attack, and illustrated the “multi-stage attack chain at a high level”:

https://www.zscaler.com/blogs/security-research/european-diplomats-targeted-spikedwine-wineloader
First, the attacker sends a malicious PDF containing a malicious link, which is clicked by the target.
By clicking on the link, a ZIP archive is downloaded from the payload hosting server. The ZIP archive contains an HTA file which, when executed, downloads another ZIP archive to the target system.
The second ZIP archive contains a DLL and an EXE file. The EXE file (sqlwriter.exe) loads the DLL to execute Wineloader. Wineloader connects to a C2 server to carry out further malicious activity.
It can be seen that there are parallels between the two attacks.
In addition, different techniques were used (Create or Modify System Process: Windows Service (T1543.003), Query Registry (T1012), System Information Discovery (T1082), Access Token Manipulation (T1134), Process Discovery (T1057), System Service Discovery (T1007), Obfuscated Files or Information (T1027), Indicator Removal: File Deletion (T1070.004), Process Injection: Thread Execution Hijacking (T1055.003) and File and Directory Discovery (T1083)).
Due to this attack, the CDU was briefly forced to take parts of its IT infrastructure offline and isolate it as a precautionary measure. In addition, the Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution and the BSI began investigations.
The German political alliance has stated that calendar data belonging to CDU chairman Friedrich Merz has been leaked. No further details can be provided due to the ongoing investigations.
CDU Detections
Mandiant offers three Yara detection rules for WINELOADER.
Yara rules are intended for the detection of malware. These are divided into the sections “Meta”, which contains information such as the author or the description, “Strings”, which contain a definition of character strings that are searched for, and the “Condition”, which must be fulfilled for the rule to be considered a hit. For example, if it says “$string1 or $string2”, only one of these previously defined strings must match for a find to be counted as a hit. An “and” can also be used here, for example.
Yara rules can be used in different ways: On security platforms, such as Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, which contains a Yara integration, MISP, VirusTotal or directly on the system.
IMPORTANT: Before this rule is executed in a production system, it should be tested and adapted on a test system.
The first rule can be used to identify files that contain obfuscated ROOTSAW payloads and thus searches for certain character strings that are typical for the obfuscation and network activity of this malware.
rule M_APT_Dropper_Rootsaw_Obfuscated
{
meta:
author = "Mandiant"
disclaimer = "This rule is meant for hunting
and is not tested to run in a production environment."
description = "Detects obfuscated ROOTSAW payloads"
strings:
$ = "function _"
$ = "new XMLHttpRequest();"
$ = "'\\x2e\\x7a\\x69\\x70'"
$ = "'\\x4f\\x70\\x65\\x6e'"
$ = "\\x43\\x3a\\x5c\\x57"
condition:
all of them
}The next Yara rule attempts to recognize the specific RC4 encryption logic in WINELOADER. RC4 encryption is a method of encrypting data by combining it with a constantly changing, seemingly random key. The system searches for specific byte sequences that are typical for the initialization and use of the RC4 algorithm.
rule M_APT_Downloader_WINELOADER_1
{
meta:
author = "Mandiant"
disclaimer = "This rule is meant for hunting and
is not tested to run in a production environment."
description = "Detects rc4 decryption logic in
WINELOADER samples"
strings:
$ = {B9 00 01 00 00 99 F7 F9 8B 44 24 [50-200]
0F B6 00 3D FF 00 00 00} // Key initialization
$ = {0F B6 00 3D FF 00 00 00} // Key size
condition:
all of them
}The Yara rule “M_APT_Downloader_WINELOADER_2” searches for a specific payload invocation stub (a small section of code contained in a malware that is specifically designed to decrypt and execute an encrypted or hidden payload). The rule looks for a specific byte sequence that is typical for the process of decrypting and executing the payload. This sequence includes operations such as loading addresses and sizes into registers, calling a decryption function and saving the decrypted address.
rule M_APT_Downloader_WINELOADER_2
{
meta:
author = "Mandiant"
disclaimer = "This rule is meant for hunting and
is not tested to run in a production environment."
description = "Detects payload invocation stub
in WINELOADER"
strings:
// 48 8D 0D ?? ?? 00 00 lea rcx, module_start
(Pointer to encrypted resource)
// 48 C7 C2 ?? ?? 00 00 mov rdx, ???? (size of encrypted source)
// E8 [4] call decryption
// 48 8D 05 [4] lea rcx, ??
// 48 8D 0D [4] lea rax, module_start (decrypted resource)
// 48 89 05 [4] mov ptr_mod, rax
//
$ = {48 8D 0D ?? ?? 00 00 48 C7 C2 ?? ?? 00 00 E8 [4]
48 8d 0D [4] 48 8D 05 [4] 48 89 05 }
condition:
all of them
}TeamViewer
TeamViewer is a remote access, control and maintenance software for various end devices such as Windows, Android, Linux, etc.
According to the latest information, the hacker group APT29 was able to log in with a compromised employee account and gain access to the system. Due to the “defense in-depth” approach, the strict separation of the corporate IT environment, the product environment and the TeamViewer connectivity platform, which does not allow lateral movement and unauthorized access, including employee data (names, business contact details and encrypted passwords for the internal corporate IT environment) were stolen.
It is still unclear which tactics and tools were used.
According to TeamViewer, the authentication processes have been strengthened to the maximum, strong safeguards have been implemented and the internal corporate IT environment has been completely rebuilt.
Customer information is therefore not affected, which is why the investigation was concluded on July 4, 2024.
TeamViewer already suffered a security incident in 2016, which was carried out by the Chinese hacker group Winnti (alias APT41). At that time, the Winnti backdoor of the same name was used.
Hunting and Queries
To find out whether APT29 is already in the system, you can use a KQL query to search for “MailItemsAccessed or SaaS actions performed by a labeled password spray IP” (Microsoft, 2024, “Midnight Blizzard: Guidance for responders on nation-state attack“)
CloudAppEvents
| where Timestamp between (startTime .. endTime)
| where isnotempty(IPTags) and not(IPTags has_any('Azure','Internal Network IP','branch office'))
| where IPTags has_any ("Brute force attacker", "Password spray attacker", "malicious", "Possible Hackers")In addition, Microsoft Sentinel has various analytic rules that can be used to detect suspicious activities in the system.
First of all, there is the possibility of identifying password sprayingagainst Entra ID applications using a query.
Another querythat searches for the authorization full_access_as_app and thus grants admin consent to OAuth application and thus access to Exchange admin mailboxes and possible sensitive data. The applications named by the query should be checked to rule out an attack and if this authorization is not required, it should be restricted.
With this query it is possible to recognize a service principle, which authorizations to add Microsoft Entra ID objects or a user account to an Admin directory role.
The following query returns OAuth applications that access emails, whether directly or via Graph. This query can be used to check whether such dual access methods correspond to the user pattern that is expected.
|
// Look for OAuth apps reading mail both via GraphAPI, and directly (not via GraphAPI)
// (one method may be legitimate and one suspect?)
let appsReadingMailDirectly = CloudAppEvents
| where Timestamp >= ago(1h)
| where ActionType == "MailItemsAccessed"
| where RawEventData has "AppId"
| extend rawData = parse_json(RawEventData)
| extend AppId = tostring(parse_json(rawData.AppId))
| where AppId != "00000003-0000-0000-c000-000000000000"
| summarize by AppId
| project-rename OAuthAppId = AppId;
let appsReadingMailViaGraphAPI = CloudAppEvents
| where Timestamp >= ago(1h)
| where ActionType == "MailItemsAccessed"
| where RawEventData has "ClientAppId"
| where RawEventData has "00000003-0000-0000-c000-000000000000" // performance check
| extend rawData = parse_json(RawEventData)
| extend AppId = tostring(parse_json(rawData.AppId))
| extend OAuthAppId = tostring(parse_json(rawData.ClientAppId)) // extract OAuthAppId
| where AppId == "00000003-0000-0000-c000-000000000000"
| summarize by OAuthAppId;
// Applications reading mail both directly and via GraphAPI
// (one method may be legitimate and one suspect?)
appsReadingMailDirectly
| join kind = inner appsReadingMailViaGraphAPI
on OAuthAppId
| project OAuthAppId
If your system is attacked by Cozy Bear, the names “Midnight Blizzard activity group” and “Midnight Blizzard attack group payload” will be displayed in the Security Center
Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures
CVE-2023-42793 - JetBrains TeamCity
CVE-2023-42793 is a remote code execution vulnerability in the JetBrains TeamCity integration and deployment platform. The remote code execution is caused by an insecure deserialization of data in certain API endpoints, which can lead to unauthorized changes to build configurations and the theft of sensitive information.
All versions prior to TeamCity 2023.05.4 are affected. A check and, if necessary, an update are necessary to keep the risk of an attack as low as possible.
CVE-2023-38831 - WinRaR
CVE-2023-38831 affects the WinRaR compression and archiving tool. The vulnerability arises from insecure processing of pathnames in archive files, which can lead to the execution of malicious code when users extract a specially crafted archive file. This vulnerability can be used to gain control of the system, steal data or damage systems.
All versions prior to WinRAR 6.23 are affected.
CVE-2019-1978 - Citrix Application Delivery Controller (ADC)
CVE-2019-19781 is a critical vulnerability in the Citrix Application Delivery Controller (ADC) and Citrix Gateway. It allows remote code execution through insecure processing of input in certain endpoints. This can lead to complete control over the ADC or gateway, allowing attackers to infiltrate networks, steal data or disrupt services.
As this vulnerability affects different versions, it is difficult to make a blanket statement, but it can generally be assumed that all versions prior to the patches in January 2020 are affected.
CVE-2020-0688 - Microsoft Exchange Server
CVE-2020-0688 affects Microsoft Exchange Server and results from the insecure processing of deserialization operations in the Exchange Control Panel (ECP) components and can lead to a complete compromise of the Exchange server, including access to all emails and the execution of arbitrary code.
This CVE mainly affects versions prior to the February 2020 patches.

https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/en-US/vulnerability/CVE-2020-0688
Measures
There are various ways to protect yourself from hacker groups such as APT29. It's important to educate users about these methods to prevent them from clicking on phishing links or entering their credentials carelessly. This makes it significantly more difficult for attackers to gain access.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a crucial topic in this context. For example, in addition to a password, a one-time token can be sent to the user. Another MFA option is the use of passkeys. These are hardware keys that are inserted into the end device, requiring the user to authenticate themselves. A more detailed explanation of passkeys and how to set them up, from both the administrator's and the user's perspective, can be found here.
In addition, Endpoint Protection or advanced anti-malware solutions and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) systems offer the possibility to detect and prevent suspicious activity on endpoints.
The implementation of role-based access control (RBAC), which restricts access to sensitive data and systems, and security policies, which develop and enforce comprehensive security policies and protocols, are also ways to minimize the risk of an attack.
More in-depth topics such as the segmentation of the network, as in the case of TeamViewer for example, or the monitoring of this, the risk of important data being lost is also lower and it is also possible to check whether external IPs have accessed the system.

Similar hacker groups
In addition to APT29 (alias Cozy Bear), there are four other hacker groups acting on behalf of the Russian government. These include Fancy Bear, which has also been classified as an APT (APT29), Voodoo Bear, which is primarily known as Sandworm, Primitive Bear and Venomous Bear.
Fancy Bear (APT28)
Alias: Fancy Bear, APT28, IRON TWILIGHT, SNAKEMACKEREL, Swallowtail, Group 74, Sednit, Sofacy, Pawn Storm, STRONTIUM, Tsar Team, Threat Group-4127, TG-4127, Forest Blizzard, FROZENLAKE
APT28 is also a constant threat alongside APT29, but unlike APT29 it is not subordinate to the Russian Foreign Intelligence Service (SVR), but to Russian military intelligence (GRU) or the Ministry of Defense. In addition to Ukraine and NATO, the group is also interested in Europe, South America, the Middle East and Central Asia.
There is also interest in various sectors such as government, military and defense, energy, finance, heavy industry, high-tech and telecommunications, higher education, news media, NGOs, and shipping and rail transport
Fancy Bear uses TTPs such as xTunnel, Mimikatz or Evil-Twin.
Voodoo Bear (Sandworm)
Alias: ELECTRUM, Telebots, IRON VIKING, BlackEnergy (Group), Quedagh, Voodoo Bear, IRIDIUM, Seashell Blizzard, FROZENBARENTS, Sandworm, APT44
Voodoo Bear, which is primarily known as Sandworm, is presumably subordinate to the GRU, just like APT28. These were also classified as an Advanced Persistent Threat, as APT44, in April 2024
There is also interest in various sectors such as government, military and defense, energy, finance, heavy industry, high-tech and telecommunications, higher education, news media, NGOs and shipping and rail transport.
Voodoo Bear uses TTPs such as AcidRaid, CaddyWiper and Mimikatz, File and Directory Discovery, Data Destruction, Disk Content Wipe and system reboot
Primitive Bear
Alias: IRON TILDEN, Primitive Bear, ACTINIUM, Armageddon, Shuckworm, DEV-0157, Aqua Blizzard, Gamaredon Group
Primitive Bear is also a Russian state-sponsored hacking group that has been linked to the Russian Federal Security Service (FSB). Just like Voodoo Bear, the main target is Ukraine, including government agencies, the military, non-governmental organizations, the judiciary, law enforcement agencies and non-profit organizations, as well as institutions related to Ukrainian affairs. This group also relied on espionage and exfiltration of sensitive data
Primitive Bear uses TTPs such as spear phishing emails, VBScripts, Ping, PowerPunch, Pterodo, QuietSieve, DinoTrain, DesertDown, DilongTrash, ObfuBerry and ObfuMerry
Venomous Bear
Alias: IRON HUNTER, Group 88, Waterbug, WhiteBear, Snake, Krypton, Venomous Bear, Secret Blizzard, BELUGASTURGEON, Turla
Venomous Bear is primarily known as Turla and, like Primitive Bear, is subordinate to the Russian Federal Security Service (FSB). According to Google, the group is primarily interested in Ukraine, NATO, Australia, South America, the Middle East and South-East Asia.
There is also interest in various sectors such as government, military and defense, higher education, news media and NGOs
Venomous Bear uses TTPs such as KOPILUWAK, QUIETCANARY, ANDROMEDA, Brute Force, Lateral Tool Transfer, Command and Scripting Interpreter: Python or Password Policy Discovery
Energetic Bear
Alias: TEMP.Isotope, DYMALLOY, Berserk Bear, TG-4192, Crouching Yeti, IRON LIBERTY, Energetic Bear, Ghost Blizzard, BROMINE, Dragonfly
Energetic is another Russian state-sponsored hacker group which, like Venomous and Primitive Bear, also belongs to the Federal Security Service of the Russian Federation (FSB). This group is active worldwide.
As the name suggests, the sector most likely to be affected is the energy sector. However, the sectors Chemicals, Communications Infrastructure, Consumer Retail: Hardline (Consumer Durables), Defense Industrial Base, Digital, Print and Broadcast Media, Education: Higher Education, Financial, Services, Healthcare & Public Health, Transportation Systems: Aviation are also affected
Energetic Bear uses tools such as Trojan.Karagany, Backdoor.Oldrea and CrackMapExec, and the techniques used include account manipulation, password cracking and supply chain compromise.
Ember Bear
Alias: Saint Bear, Lorec Bear, Bleeding Bear, DEV-0586, UNC2589, UAC-0056, Lorec53, Ember Bear
Just like Fancy Bear and Voodoo Bear, Ember Bear is probably part of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation (GRU). In addition to Ukraine and Georgia, Western Europe and North America are also targets of the attacks.
The three sectors are mainly target ministries, pharmaceutical companies, and financial sector
According to MITRE, the tools that could be tracked are ATT&CK WhisperGate, Saint Bot, OutSteel, as well as techniques such as Software Packing, User Execution: Malicious File, Exploitation for Client Execution
Boulder Bear
Alias: -
Another hacker group that can be linked to the Russian state is Boulder Bear. There is virtually no information on this, except that it is possibly subordinate to the Federal Security Service of the Russian Federation (FSB).
Countries or sectors at risk, as well as TTPs, are unfortunately not known.
For further research
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QSVQR_7fAFQ
https://attack.mitre.org/groups/G0016/
https://malpedia.caad.fkie.fraunhofer.de/actor/apt29
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cozy_Bear
https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/threat-intelligence/unc2452-merged-into-apt29?hl=en
https://www.zscaler.com/blogs/security-research/european-diplomats-targeted-spikedwine-wineloader
https://www.dw.com/en/germany-major-hack-targets-center-right-cdu-party/a-69242147
https://www.teamviewer.com/nl/resources/trust-center/statement/
https://vulncheck.com/blog/how-we-think-about-threat-actors
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/en-US/vulnerability/CVE-2020-0688
https://apt-ecosystem.com/russia/map/
Image by Jefferson Santos from unsplash.com



